HA(High-Availability)
- Aims to ensure an agreed level of operational performance, usually uptime, for a higher than normal period
FT(Fault-Tolerance)
- Property that enables system to continue operating properly in the event of the failure of some of its components
DR(Disaster-Recovery)
- a set of policies, tools, procedures to enable the recovery or continuation of vital technology infrastructure and systems following a natural or human-induced disaster
Summary
- HA: Minimize any outages
- FT: Operate through faults
- DR: Used when these don’t work
Route53
Route53 allows you:
- register domain
- host zones files on managed name service
Global service but only 1 database
Route 53 is globally resilient
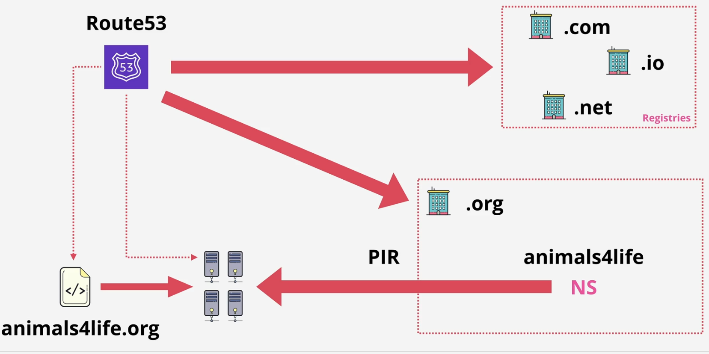
Register Domain
- route 53 checks for the registry for that top level domain, if it is available
- route 53 creates a zone file(hosted zone) for the domain being registered(zone file: a database contains all DNS information of the domain)
- allocates name service for this zone
- put zone file onto the 4 managed name servers
- connect top level domain registry and add the name server records into the zone file for the (.org or .com or .io or .net) top level domain
- you can register a domain using route 53, and put the zone file out side of the AWS name servers
- you can also register a domain elsewhere and created hosted zone in route 53 and point the external domain as the route 53 name servers
Diagram:
DNS Records Types
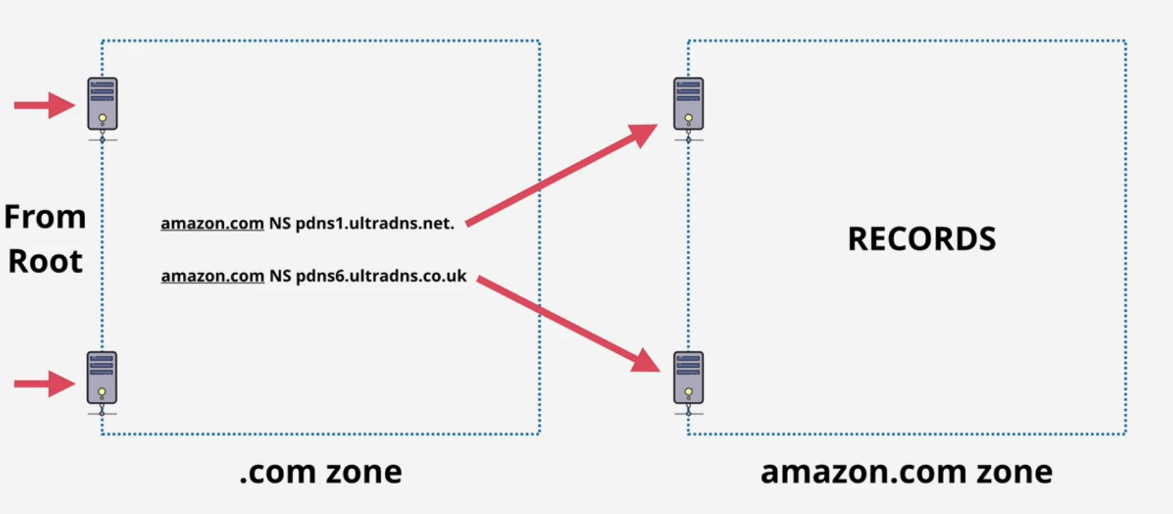
Nameserver: nameserver inside a zone, point to the servers host subzone:
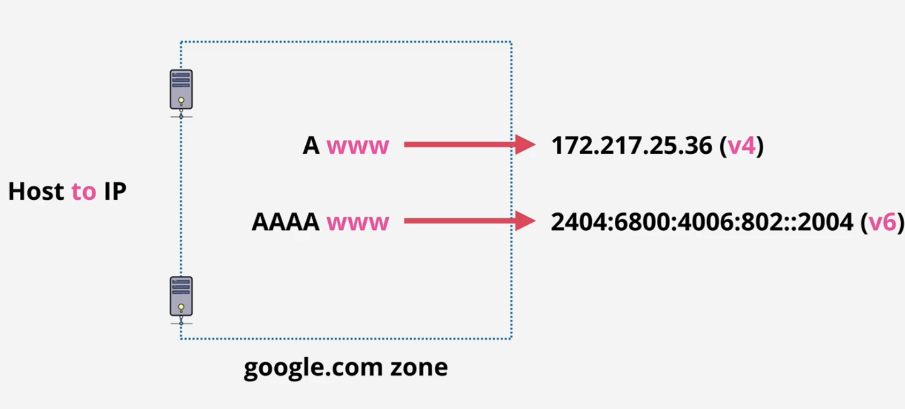
A and AAAA records: host name for IP address directly. A to IPv4, AAAA to IPv6. Normally, we will create 2 records for the same name(1 for A, another for AAAA):
- CNAME Records: This type of record creates an alias for an A record. It points one domain name to another domain name:
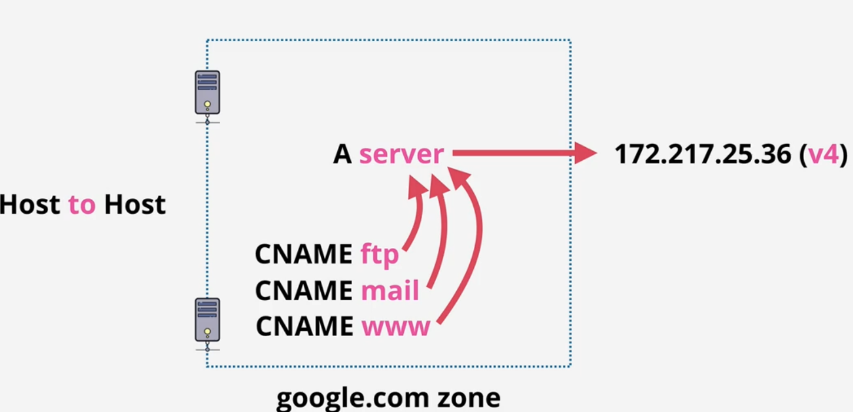
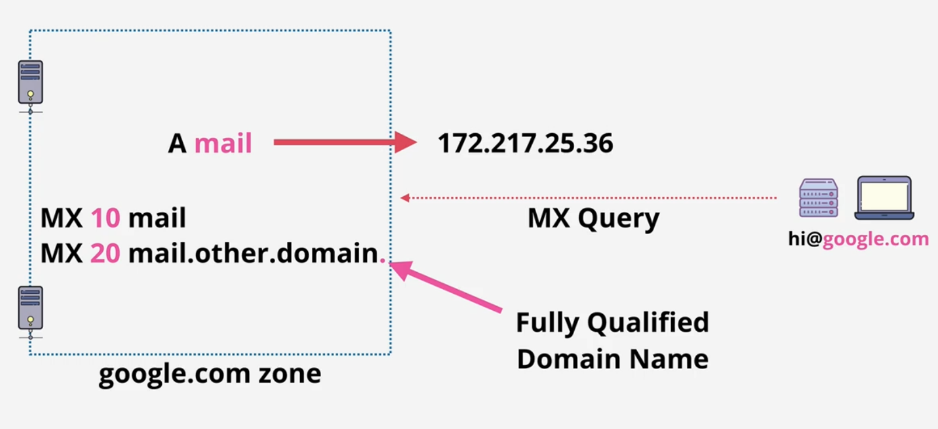
MX Records(important for email): A n A record named “mail” inside. Email server looks at 2 addresses of the mail(hi@google.com), focus on the domain: google.com, then using MX query on goole.com:
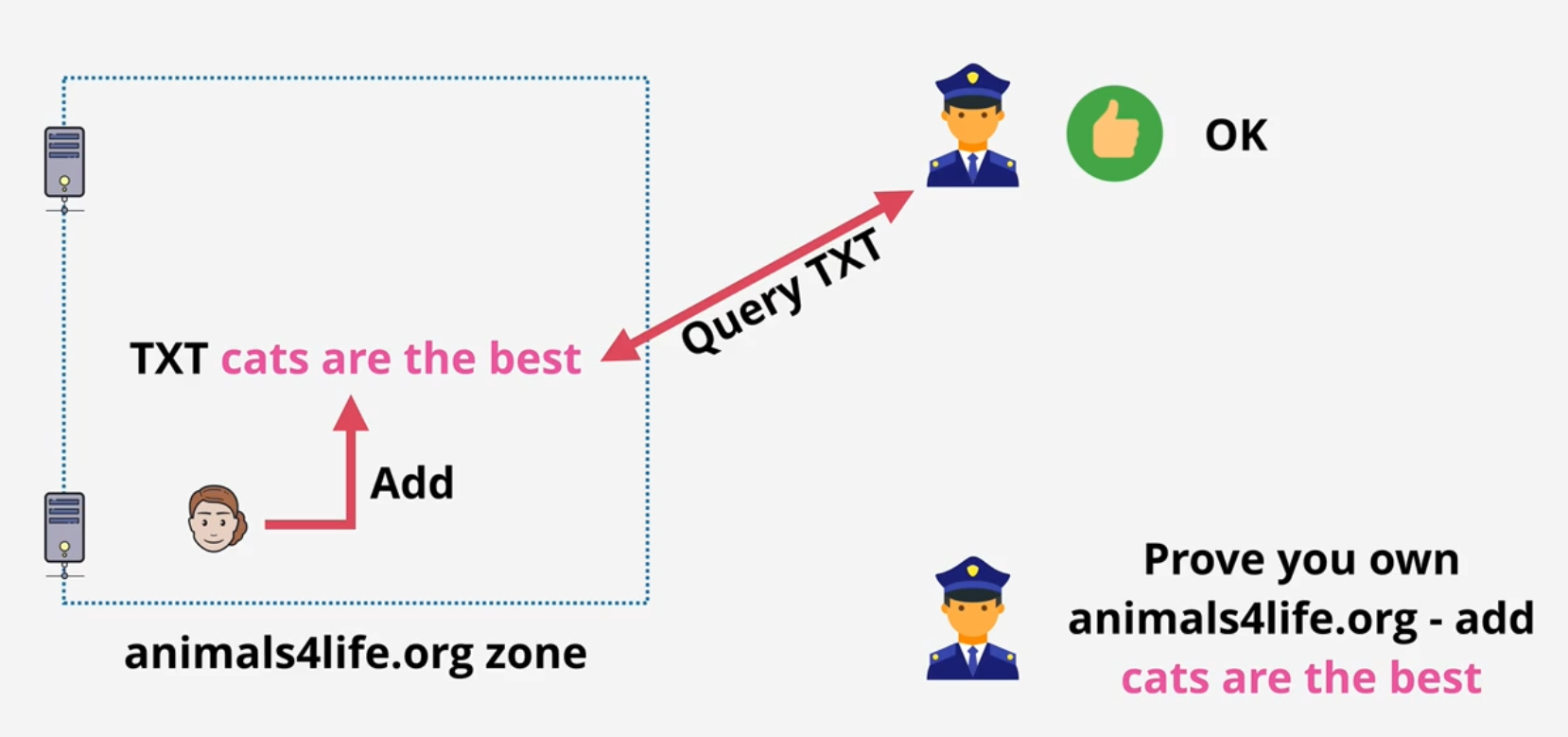
TXT Records: allows you to add arbitrary text to a domain, often used in domain name verification