What is Routing in express
Routing is the mapping relation between client requests and server’s response functions
The routing is consist of 3 parts: requesting type, requesting url address, response functions
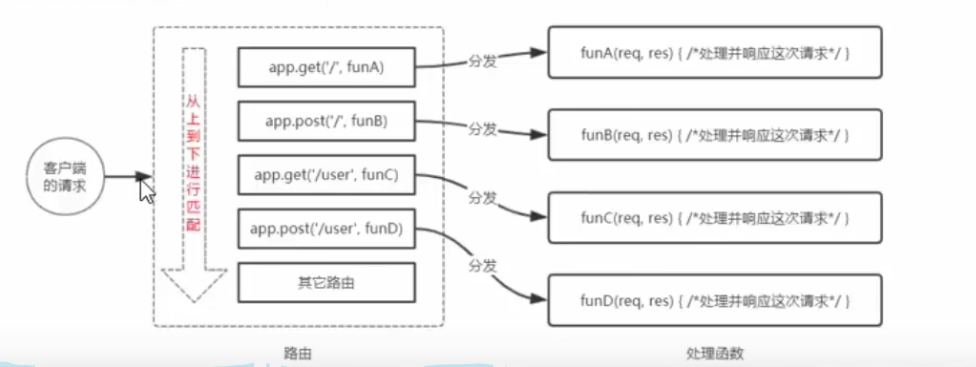
Routing matching process
Once a request reaches the server, express would start to match the requesting according to its type and url from top to bottom and deliver the request to the proper response function.
Modulization of routing
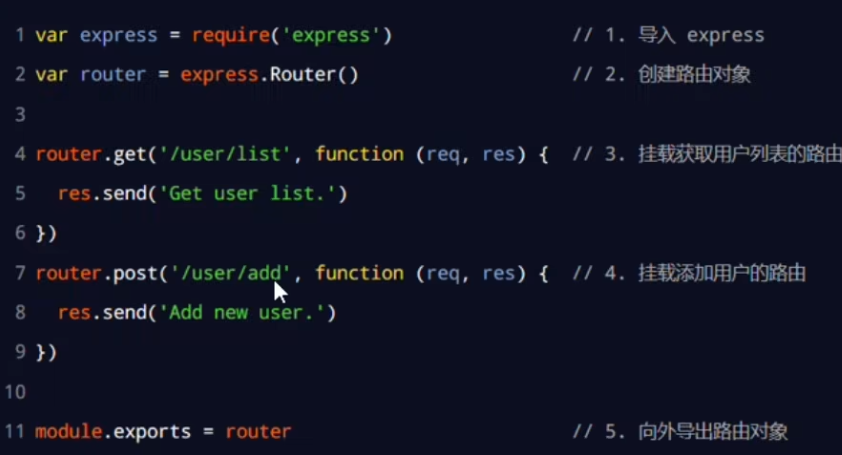
1. Create .js file to store router
2. Create router object by express.Router()
3. Mount specific router on the object
4. Export router by module.exports
5. Use app.use() to register router in app.js

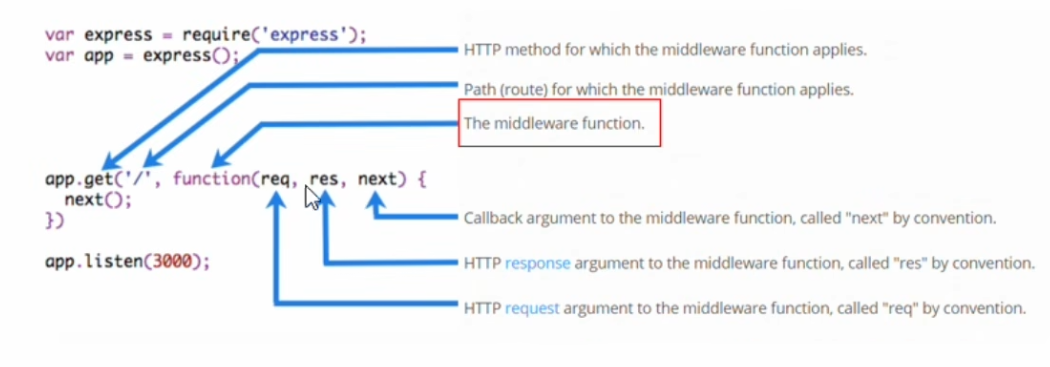
Middleware
The middleware is a function that is added a next param compare to a response function.
next(): passing the request to the next middleware or router
Global middleware
Simple use
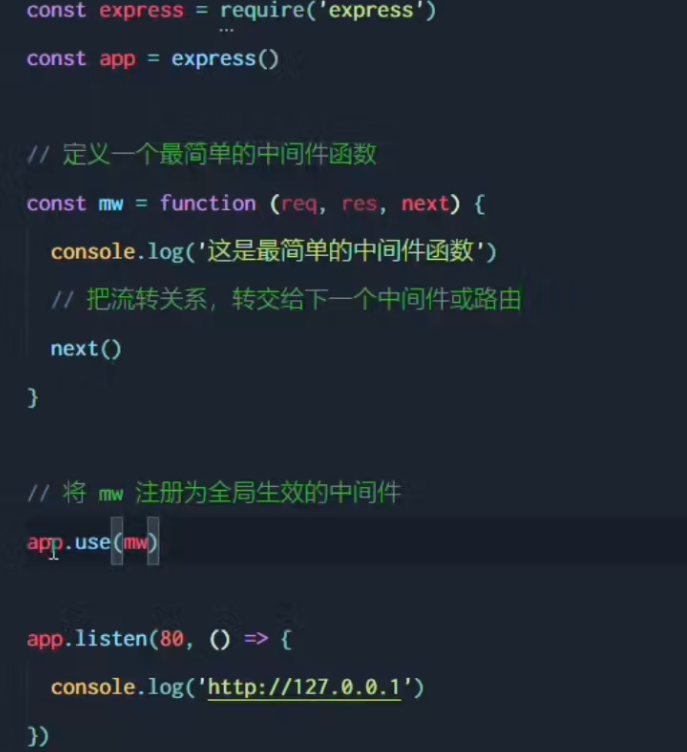
In multiple middlewares and routers, req and res object are shared
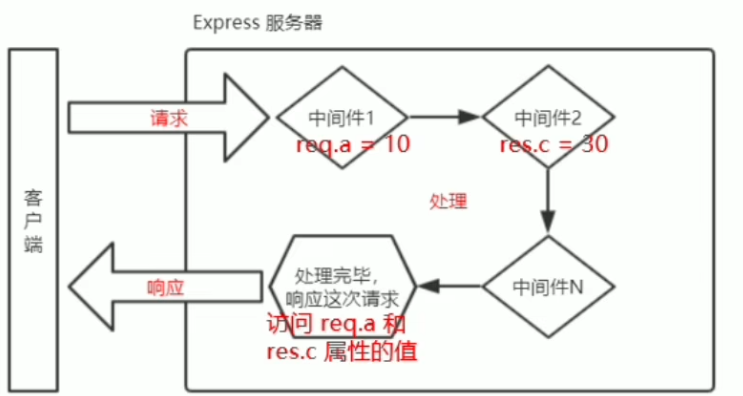
Declare multiple global middlewares

Local Middleware
Simple use
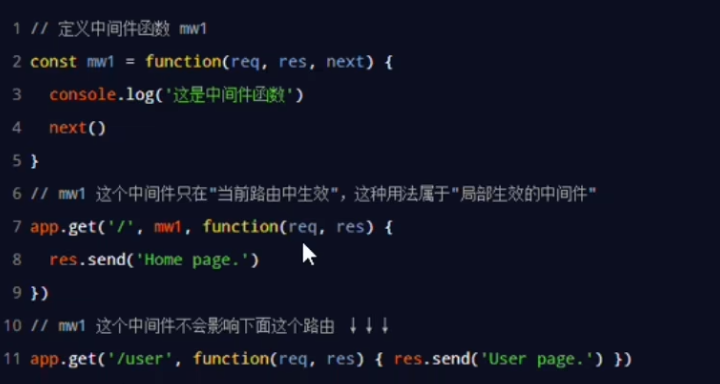
Declare multiple local middlewares

Attention Points on Middleware
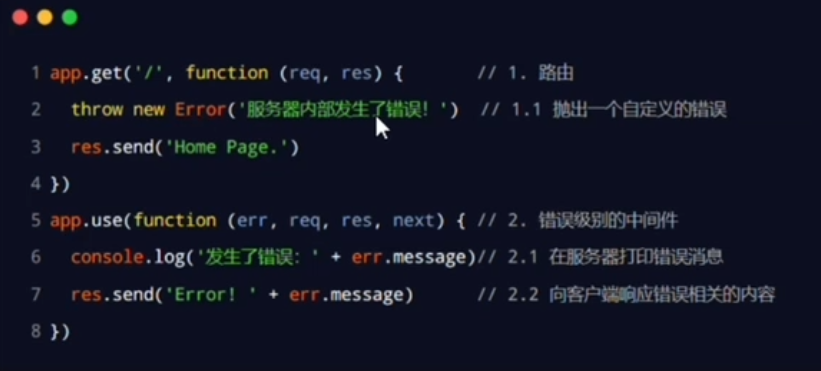
1. Must register middlewares before routers(except error middlewares)
2. Invoke next() in the end of middlewares
3. req and res objects are shared among middlewares
Error Middleware
Simple use
Express Built-In Middlewares
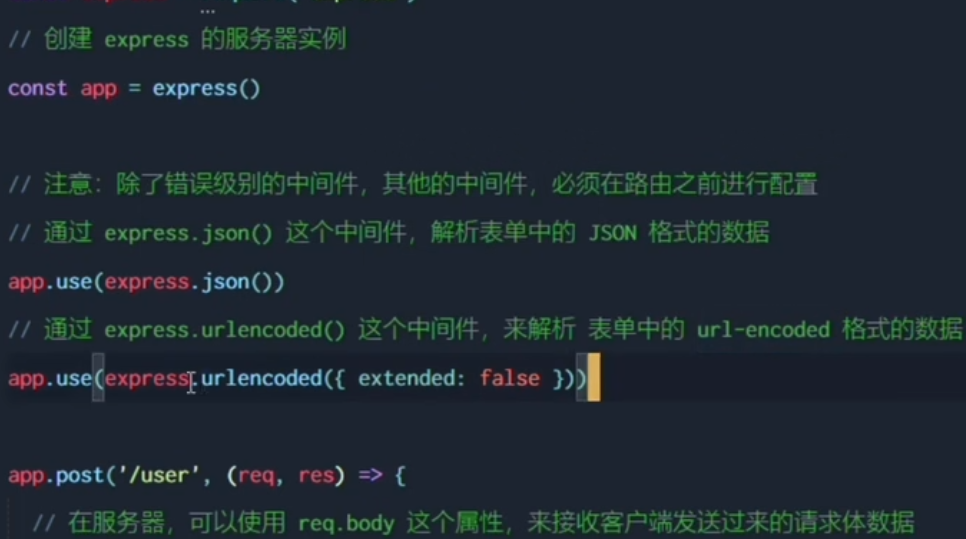
1. express.static
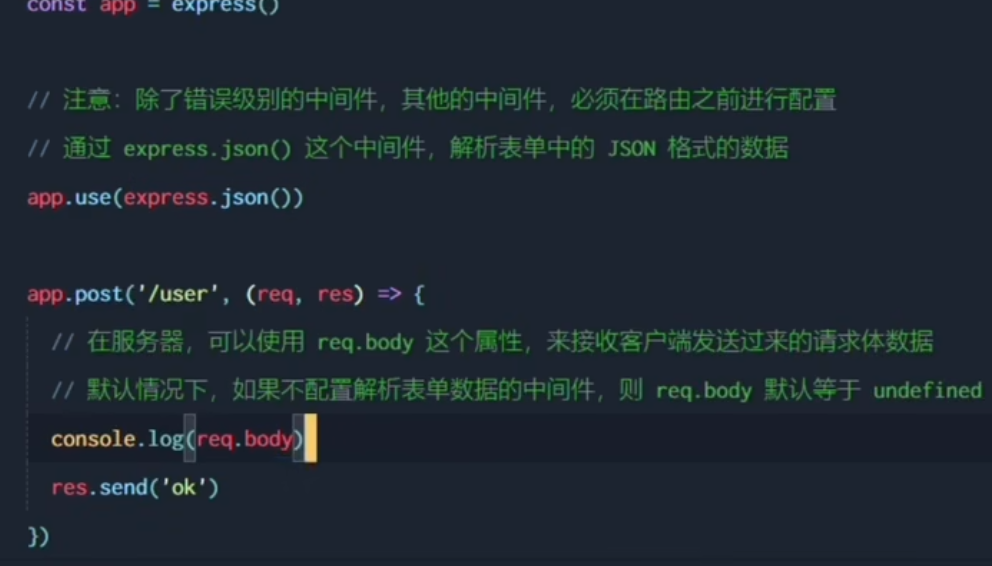
2. express.json
By default, req.body would be undefined unless there is a middleware used to analyze req data
Simple use
3. express.urlencoded
Simple use
An Example of Using Middleware
server monitor and receive data in middleware in client, parse and pass them to the router which returns the same data to the client
const express = require('express');
const {parse} = require('querystring')
const app = express();
app.use((req, res, next) => {
let str = ''
req.on('data', (chunk) => {
str += chunk
})
req.on('end', ()=> {
const body = parse(str)
req.body = body
next()
})
})
app.post('/user', (req, res) => {
res.send(req.body)
})
app.listen(8888, () => {
console.log('server runing');
})
Cors
yarn add cors
const cors = require('cors')
app.use(cors())

